Orchestrating open-source RPA with Camunda Cloud
RCC is a really cool command…
In January 2023, together with Niall Deehan, we hosted RoboCon 2023 workshop Business process automation with Robot Framework and Camunda Platform. The workshop was based as much as possible on open source. Even the development environment was a pre-built Linux-desktop ensuring equal experience for the participants.
But something we may not have emphasized enough: all the open source automation learned at the workshop, is also compatible with Camunda Platform SaaS, and even for implementing RPA on Windows!
Open-source Windows RPA
To get started with Robocorp RCC based open-source automation on Windows, one can choose between two alternative development experiences:
-
VSCode with Robocorp extensions provides professional development experience for all kinds of RCC driven automation, both in Robot Framework and/or in Python.
-
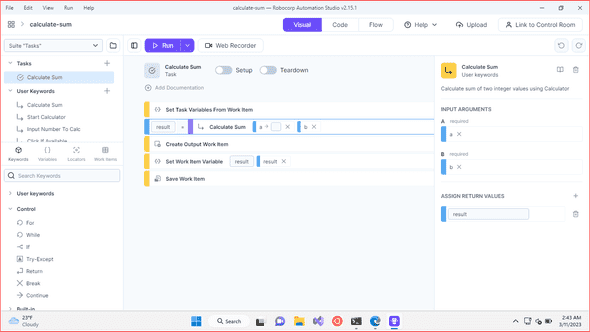
Robocorp Automation Studio is a standalone low code development tool for implementing the most common use-cases for Robot Framework based automation.
Starting with Automation Studio is the easiest and safest choice, because any project started with Automation Studio, could be later continued and developed further with VSCode.
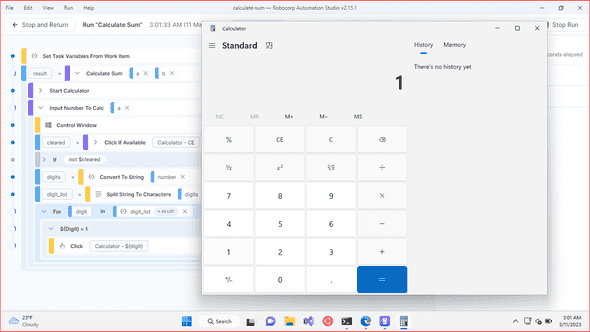
Here’s a downloadable example RPA Calculator bot based on a Automation Studio template for Windows automation. It’s a dummy bot to calculate sum of two input variables by automating Windows Calculator app. Yet, it is ready to be orchestrated using Camunda Platform. Just unzip the package, open its folder in Automation Studio, try it out, and zip its contents back for deployment.
Camunda Platform SaaS as orchestrator
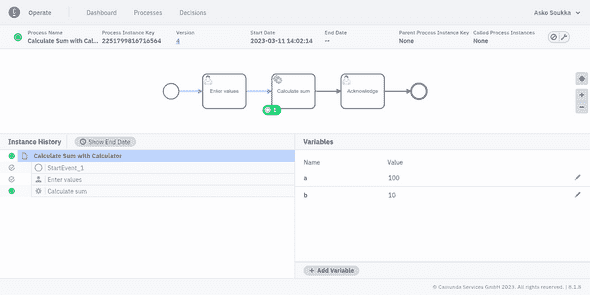
Now, that we have a bot, the next thing is to integrate it with Camunda Platform SaaS. Here is a simple example process:
- It provides user taks form for asking the input values,
- orchestrates the RPA bot for the task, and
- displays the results through an another user task form.
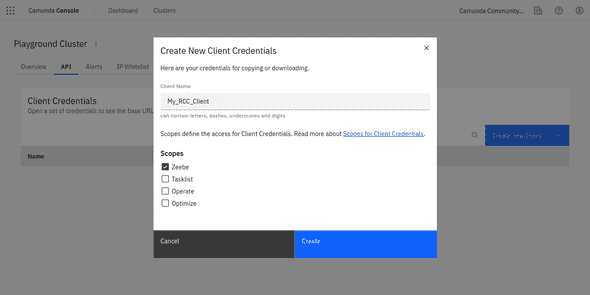
To continue, it is required to have client credentials for the cluster with scope Zeebe. Those could be use to deploy the process to the cluster using Camunda Desktop Modeler. The credentials are also required for integrating RCC bots with the running processes.
Make sure to download or save the information shown after creating new credentials. Client secret is only shown right after creation, but also client id, cluster id and cluster region are required for running the integration.
Once the process is deployed (either using the cloud or desktop modeler), at least one instance of it has been started, and the first user task has been completed, everything is ready for the RCC automation part.
Running RCC integration
Integrating an RCC bot with Camunda Platform requires some preparation. But not much! The following integration is based on parrot-rcc (an open source pyzeebe based Zeebe client), which delegates Camunda Platform tasks to be run by RCC.
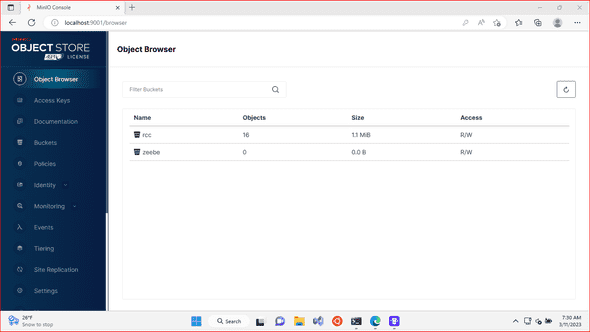
The integration has prerequisite of two writable buckets at S3 compatible object storage for storing execution logs and possible file payloads. For development purposes, the easiest way is to download MinIO executable and run it locally.
For example, with
.\minio.exe server C:\minio --console-address :9001as in
PS C:\Users\User\Downloads> .\minio.exe server C:\minio --console-address :9001
WARNING: Detected default credentials 'minioadmin:minioadmin', we recommend that you change these values with 'MINIO_ROOT_USER' and 'MINIO_ROOT_PASSWORD' environment variables
MinIO Object Storage Server
Copyright: 2015-2023 MinIO, Inc.
License: GNU AGPLv3 <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/agpl-3.0.html>
Version: RELEASE.2023-03-09T23-16-13Z (go1.19.7 windows/amd64)
Status: 1 Online, 0 Offline.
API: http://10.0.2.15:9000 http://127.0.0.1:9000
RootUser: minioadmin
RootPass: minioadmin
Console: http://10.0.2.15:9001 http://127.0.0.1:9001
RootUser: minioadmin
RootPass: minioadmin
Command-line: https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/reference/minio-mc.html#quickstart
$ mc.exe alias set myminio http://10.0.2.15:9000 minioadmin minioadmin
Documentation: https://min.io/docs/minio/linux/index.html
Warning: The standard parity is set to 0. This can lead to data loss.By its default configuration parrot-rcc expects two writable buckets, rcc for logs and zeebe for file payloads, to be available at the configured storage. For MinIO those may be created easily through its web console (for example at http://localhost:9001/ with the default user minioadmin and password minioadmin).
Next, RCC must be downloaded. Similary to MinIO, RCC is just a simple binary, runnable as such, without any extra installation required. RCC is used for executing parrot-rcc, and then parrot-rcc is also using RCC for executing the automation tasks.
The final step requires creation of two configuration files. At first, conda.yaml, which defines an RCC runtime environment with a known good version of parrot-rcc installed:
channels
conda-forge
dependencies
python=3.9.13
pip=22.1.2
pip
https://github.com/datakurre/parrot-rcc/archive/46553ce2f73d14fa46a9188802d59e645a106a19.tar.gzAnd then, robots.yaml, which instructs RCC to actually execute parrot-rcc in that environment:
tasks
RCC
shellparrot-rcc
condaConfigFileconda.yaml
artifactsDiroutput
PATH
.
PYTHONPATH
.
ignoreFiles
.gitignoreAll done!
Now, it is only required to execute rcc run (for parrot-rcc) with the required configuration arguments for connecting to Camunda Platform SaaS and locating our zipped RPA bots. For example, with
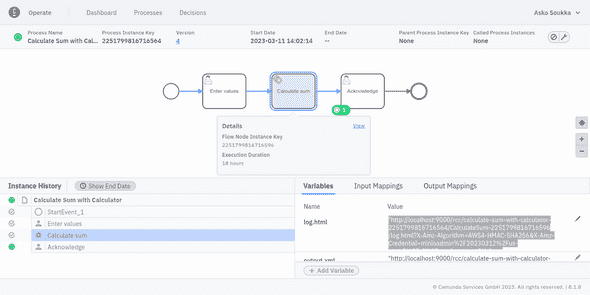
c:\Users\User\Downloads\rcc.exe run -- --rcc-executable=c:\Users\User\Downloads\rcc.exe --camunda-client-id=MY_CLIENT_ID --camunda-client-secret=MY_CLIENT_SECRET --camunda-cluster-id=CAMUNDA_CLUSTER_ID --camunda-region=CAMUNDA_CLUSTER_REGION --log-level=debug --rcc-fixed-spaces c:\Users\User\Downloads\calculate-sum.zipRCC will start parrot-rcc, which reads zipped bots, connects to Camunda Platform, waits for tasks matching the bots, executes the bots, and returns their output work items back to Camunda as variables in local scope of the executed tasks.
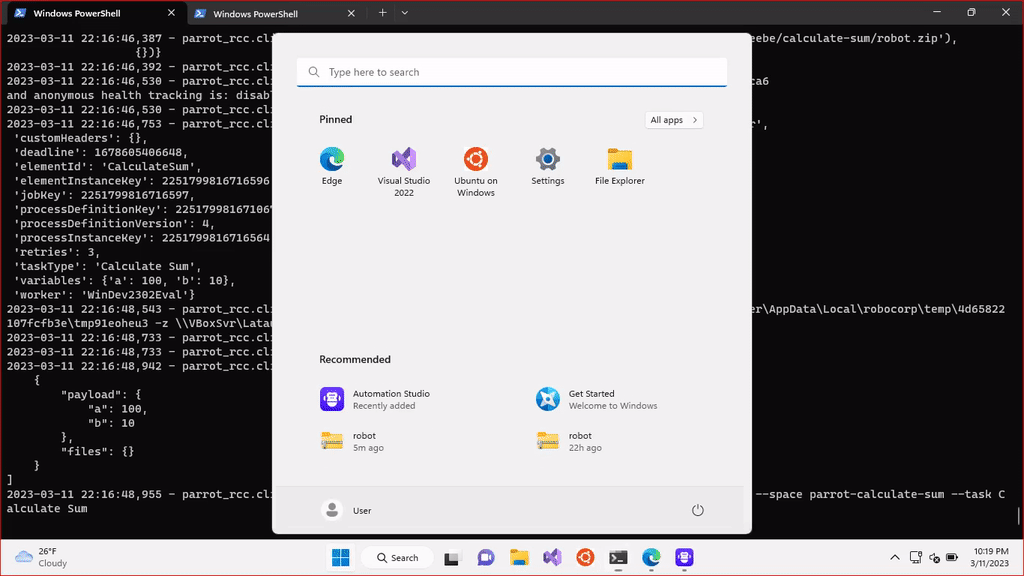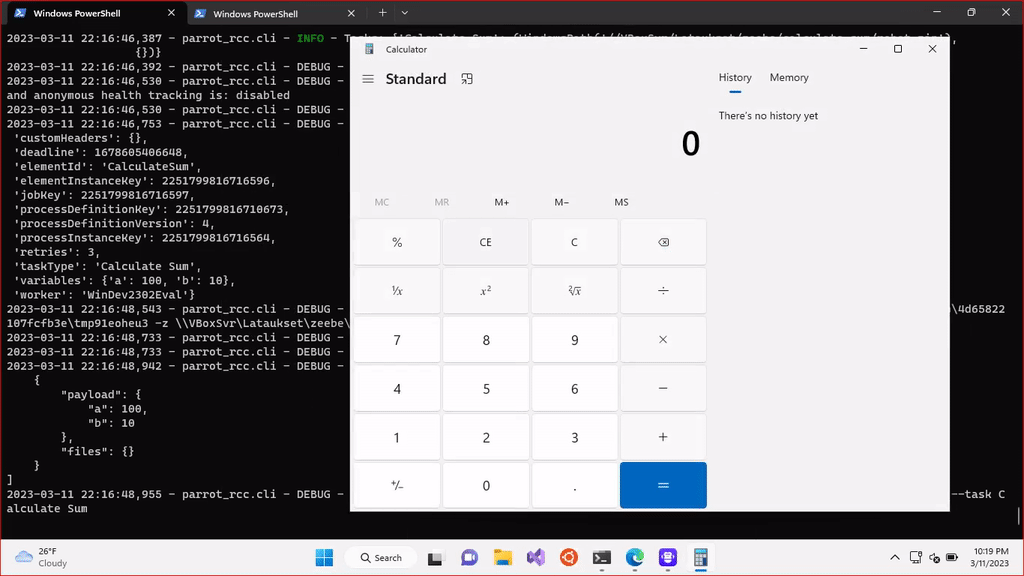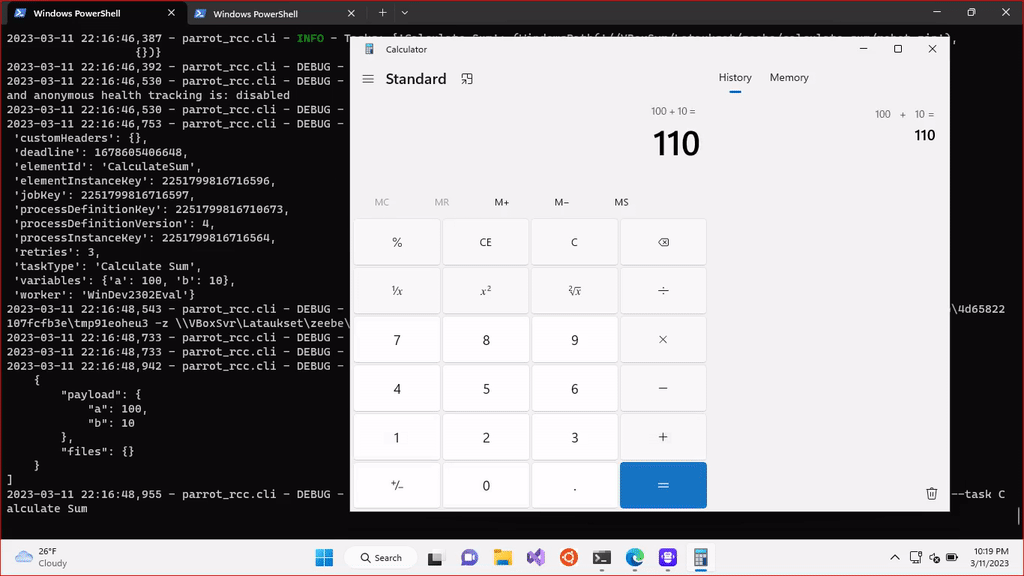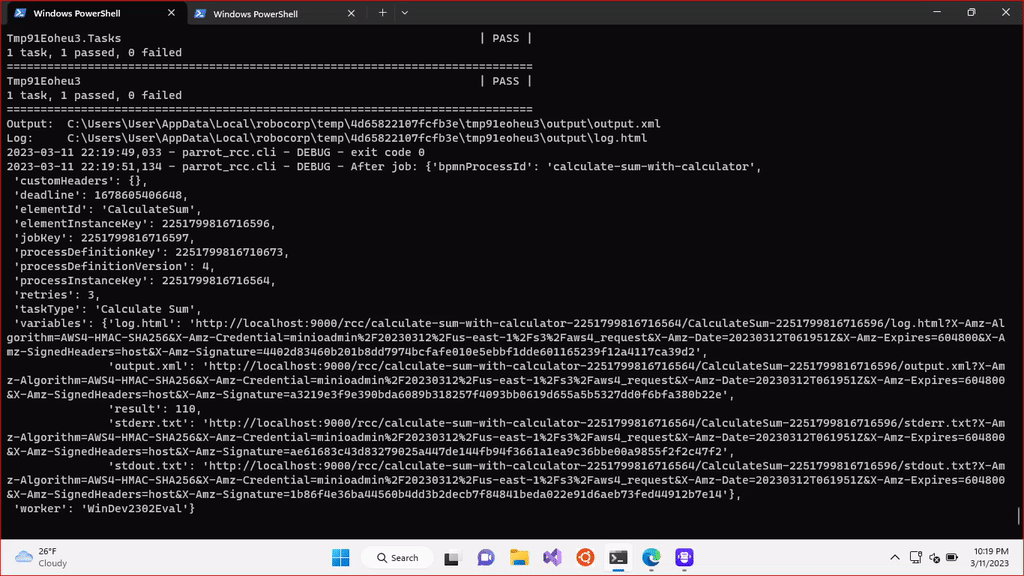
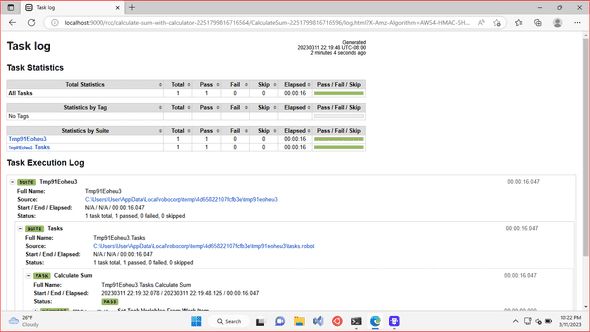
In addition to the output work item variables, the RCC integration also saves links to RPA execution logs as task scoped variables. This should really help validating that bots did the right thing, and debug them when something goes weird.
Further reading
If you got interested, there’s much online material for learning more and filling the gaps left into this introduction:
-
Robocorp Quickstart Guide is the portal for all the official resources on RCC based automation. Just remember, that with Camunda Platform and the RCC integration shown here, you may not need to use their cloud offering at all.
-
Our RoboCon 2023 automation workshop materials remain to be available. They describe in detailed examples, how to configure BPMN tasks for RCC automation bots. Even with just Zeebe, without any Camunda cloud offerings.
-
Finally, Camunda Platform documentation, of course, is available for all the remaining BPMN or Camunda related questions.
Happy automation!